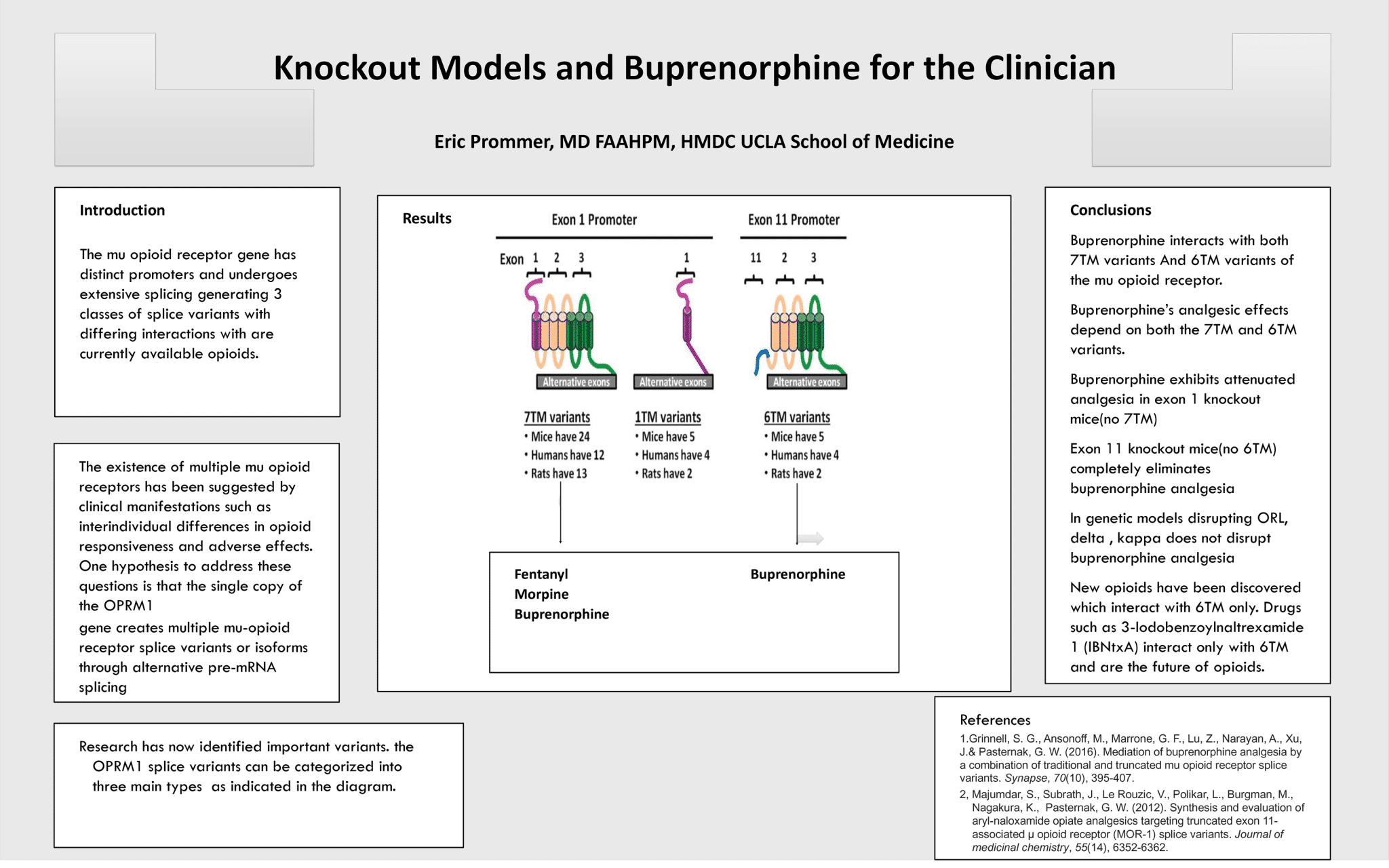
Knockout Models in Buprenorphine for the Clinician
Eric Prommer, MD, FAAHPM, HMDV UCLA School of Medicine
Poster File: Click here for Poster PDF file.
Poster File: Click here for Poster PDF file.
Abstract: Buprenorphine has recently gained more traction as a first-line agent for managing mild to moderate, constant pain in a cancer patient population. This case represents a patient who participated in a Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell trial while receiving high-dose (32 mg/day) buprenorphine for pain associated with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Pain increased immediately after receiving CAR T-cell treatment but was not responding to rapidly escalating doses of hydromorphone via a patient-controlled analgesia device. Supportive Medicine (Palliative Care) was consulted to address pain management in the context of suspected competitive inhibition of opioid agonists by high-dose buprenorphine. The decision was made to stop buprenorphine and start methadone, using the buprenorphine to morphine ratios published by Safer Care Victoria, a program from the state health service of Victoria, Australia, and the morphine to methadone ratio recommended by McPherson. The patient was successfully discharged from the hospital 6 days after methadone initiation, starting at 10 mg every 8 hours and discharging with 20 mg every 12 hours. Breakthrough pain was relieved with hydromorphone 6 to 8 mg every 3 hours as needed at the time of discharge. There was significant improvement in response to breakthrough opioids after stopping buprenorphine.
Poster Handouts: Click here to access the poster handouts.
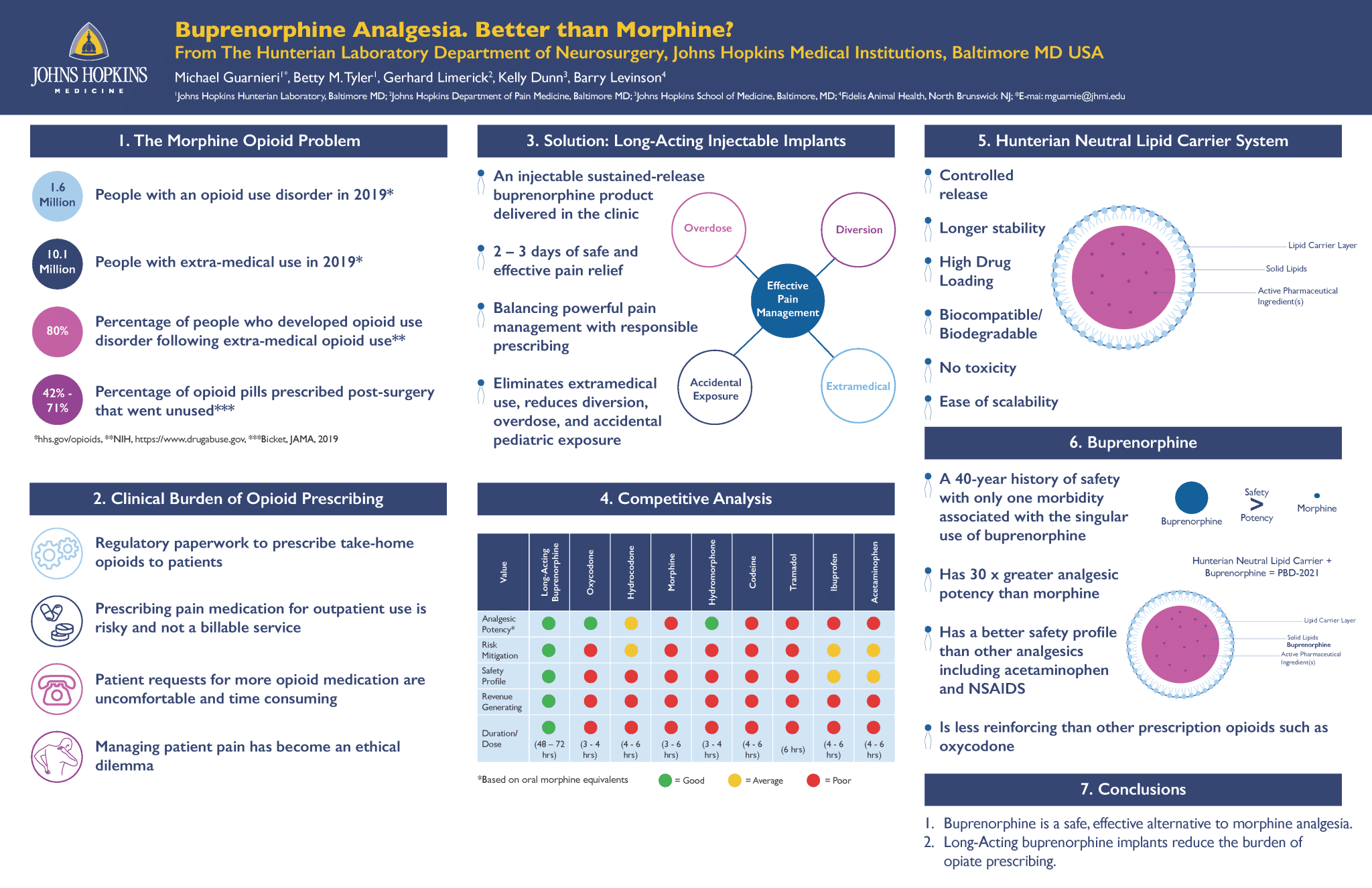
1 Johns Hopkins Hunterian Laboratory, Baltimore MD; 2 Johns Hopkins Department of Pain Medicine, Baltimore MD;
3 Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 4 Fidelis Animal Health, North Brunswick NJ; *E-mail: mguarnie@jhmi.edu
The Hunterian Laboratory Department of Neurosurgery, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore MD USA
Poster File: Click here for Poster PDF file.
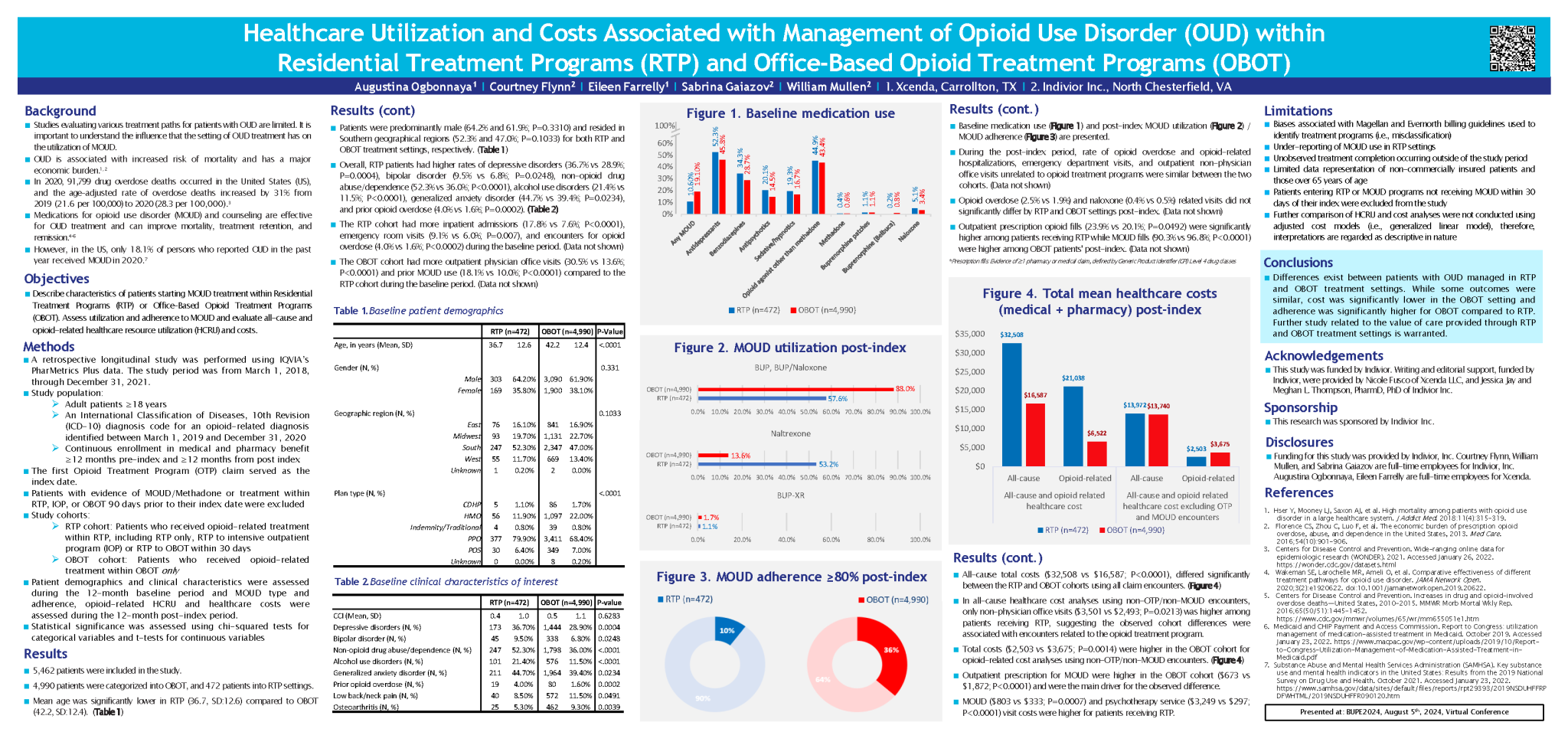
This study examines the utilization of MOUD in different opioid treatment programs as well as to explore differences in adherence, persistence and all-cause and opioid related health-care resource utilization. Costs associated with opioid treatment programs (OTP) are not extensively studied.
Poster File: Click here for Poster PDF file.
The Human-AI Interface: Unveiling Novel Qualitative Strategies For Enhancing Opioid Use Disorder Treatment Decisions
Serena Mani, MPH, Thomas Wojda, MD, MBA
This study explores the use of ChatGPT for optimizing opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment through prompt engineering techniques. By leveraging methods such as Chain of Thought, contextual, and zero-shot prompting, the research aims to enhance clinical decision-making and tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs, improving OUD management outcomes.
Our findings indicate AI-driven decision support can optimize OUD treatment, highlighting the potential and limitations of integrating AI into clinical practice.
Poster File: Click here for Poster PDF file.
A Review of the Primary and Secondary Outcomes From a Phase I Study Comparing the Respiratory Effects of Buprenorphine Buccal Film and Oral Oxycodone Hydrochloride Administration
Lynn Webster, MD, Matthew Maga, PhD
A review of the primary result of the phase 1 placebo-controlled study is presented: buprenorphine buccal film did not significantly reduce respiratory drive, while oxycodone resulted in a significant dose-dependent decrease in respiratory drive; secondary results showed several other important differences between BBF and oxycodone.
Overdose by respiratory depression, from abuse or medical use, is a major concern with opioids. Buprenorphine buccal film (BBF) is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist that, unlike full μ-opioid receptor agonists, has shown a ceiling effect on respiratory depression.
Poster – Evaluation of Strategies to Enhance Hospice Patient and Family’s Knowledge
and Confidence of Commonly Used Medications
Abby Stevens, PharmD1,2, Ryan Costantino PharmD, MS, BCPS, BCGP1, Mary Lynn McPherson, PharmD, MA, MDE, BCPS1
1 University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, 2 MedStar Health
Background:
Approximately 50% of the patient deaths of those enrolled in hospice care in 2018, died at home.1
• Twenty-three percent of informal caregivers (IFC) caring for patients in home hospice agreed it is difficult to decide which
analgesic to give, and 21% agreed it is difficult to decide what dose of analgesic medication to administer.2
• The Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS) hospice survey is distributed by the Centers
for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) to informal caregivers after the death of a hospice patient to evaluate eight domains of
care: communication with family, getting timely help, treating patient with respect, emotional and spiritual support, help for
pain and symptoms, training family to care for patient, rating of the hospice, willingness to recommend the hospice.3
• Infographics provide complex information to various audiences in an easy to comprehend format with the use of pictures and
images.4
Keywords: hospice, caregiver, patient, family, palliative medicine, palliative care
Presentation Slide Handout: Poster Presentation PDF
DOI: 10.5055/bupe.21.pp.0095
References:
1. NHPCO Facts and Figures 2020 Edition. National Hospice and Palliative
Care Organization. 2020 Aug 20.
2. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2004;27(2):114-124.
3. CAHPS® Hospice Survey | CMS. Accessed April 11, 2021.
4. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(20):2514-2517.
Poster – Limited Observational Case Study Documenting The Transition of Patients
Off Medication-Assisted Treatment With The Use of XR-Buprenorphine
Linda Young, DNP
Owner/Provider, Compassionate Care, Inc., North Smithfield, RI 02896
Abstract:
This was a limited observational case study, documenting the reported withdrawal symptoms of three Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) patients, after the cessation of subcutaneously injected XR (extended release) buprenorphine. The participants were two females ages 39 (participant A) and 37 (participant B) and one male 40 (participant C) years old. Each participant had a diagnosis of opioid use disorder (OUD), had at least three years of documented opioid cessation, were stable in all aspects of their lives and were requesting to be transitioned off MAT. The participants were given injections of XR-buprenorphine for six consecutive months and then the treatment was discontinued. Each participant met with the clinician monthly and a COWS (clinical opioid withdrawal scale) and a urine for toxicology was obtained. The female participants were followed for twelve and eleven months respectively and the male for nine months. The results of the COWS scores were zero (0) for all consecutive months of the study and the urine tox screens were negative for opioid use for all consecutive months, for all three participants. Although the results of this case study are limited, they do indicate that the use of XR-buprenorphine to transition patients off MAT may be a novel and innovative way to assist stable patients with reclaiming their previously opioid free lives.
Keywords: Medication-assisted treatment, XR-buprenorphine, opioid use disorder, buprenorphine
Presentation Slide Handout: Poster Presentation Handouts
DOI: 10.5055/bupe.21.pp.0090
Poster – A randomised controlled study to compare analgesic efficacy of sublingual buprenorphine
versus intravenous tramadol in patients undergoing mastectomy
Krishna Sumanth Dokku, Srinivasa Shyam Prasad Mantha, Abhijit Nair, Basanth Kumar Rayani
Department of Anaesthesiology, Basavatarakam Indo- American Cancer Hospital and Research Institute, Hyderabad, India
Abstract:
Sublingual (SL) buprenorphine has been used by researchers to manage acute postoperative pain. In this study, we compared analgesic efficacy of SL buprenorphine to intravenous tramadol in managing postoperative pain after mastectomy.
Postmastectomy pain syndrome (PMPS) is a chronic neuropathic pain observed in women who undergo breast surgery. Poorly managed postoperative pain after breast surgery is one of the important causes of PMPS. Buprenorphine is available for clinical use in the form of sublingual (SL) tablets which have been used for managing acute postoperative pain with reasonable success.
Presentation Slide Handout: Poster Presentation
DOI: 10.5055/bupe.21.pp.0085
Poster – The Effects of CARA on Buprenorphine prescribing patterns amongst providers
Jonathan Liu MD, Henry Young MD
Abstract:
Background: Buprenorphine is a mainstay of FDA approved Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) used to treat OUD. Access remains a barrier to widespread treatment.
Purpose: In 2016, CARA sought to increase MAT access by allowing waivered Nurse Practitioners (NPs) and Physician Assistants (PAs) to prescribe buprenorphine for MAT. NP and PA written prescriptions have increased annually alongside the number of licensed providers. Unclear is whether increasing prescriptions can be attributed to each provider prescribing more, an increase in providers, or both. We examined the effects of CARA on prescribing patterns among advanced practice providers.
Procedures: The number of buprenorphine prescriptions written in the US by NPs, PAs, and physicians from 2012-2017 was collected using the IQVIA database, which represents 92% of all US retail prescriptions. The number of providers was obtained from the providers’ respective licensing agencies. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the data. Prescriptions per provider for PAs, NPs and physicians and physicians increased 8%, 28% and 4%, the year CARA took effect, compared to 14%, 19% and 9% the year before.
Conclusions: Total buprenorphine prescriptions and buprenorphine prescriptions per provider increased annually for all provider types. However, the prescriptions per provider increased for NPs, but decreased for PAs the year CARA was implemented.
Presentation Slide Handout: Poster Presentation PDF
DOI: 10.5055/bupe.21.pp.0080
